
Life Insurance & what you need to know
Making Life Insurance easy to understand so you can make good choices.
Table of content
2. How much life insurance cover do you need?
3. Benefits & features of life insurance
4. Different types of life insurance
Register to download the ebook below
Making Life Insurance easy to understand so you can make good choices all the time?
The world of life insurance is complex. Customers are buying an intangible product that can often be confusing and complicated with technical terminology, conditions, obligations, jargon and product documents with many pages outlining what you are or are not covered for.
So, we have developed this guide to help breakdown the confusion, jargon and complexity of the world of life Insurance and help answer questions you may have. Our aim is to make life insurance easy to understand, making it easier to make the right decisions when it comes to protecting what’s important.
1. So What is Life Insurance?
A life insurance policy is a contract between an insurance company and you (the policy owner). It’s an agreement that, in the event of your death, the insurance company will pay the sum insured to your loved ones (or to you, if you are terminally ill and expected to die within 12 months). Your cover is fully tailored and takes into account your age, medical history and personal lifestyle.
This is one of the most important types of insurance that you can have. Life insurance seeks to protect your loved one’s financial security in the case of your premature death and with many policies if you are diagnosed with a terminal illness and expected to live less than 12 months during the term of the contract.
It provides this by paying a tax fee lump sum to your dependants that can be used to reduce debt, pay off mortgage, pay for final expenses, replace your income, or provide an inheritance. The purpose of the funds are entirely yours to decide
2. How much life insurance cover do you need?
Most people with dependants need some life insurance – just in case the unthinkable happens.
At a minimum, life insurance should cover your debts, funeral expenses, full repayment of your mortgage (including any early-repayment fee), and your family's immediate living costs.
As well, you could add in the amount required to replace any lost income, or pay for a caregiver or alternative schooling arrangement, until the dependant family members are no longer dependent on your support.
Take the time to consider how much money your loved ones might need to maintain their living standards if you were to pass away. This might include costs such as bills, mortgage repayments, school fees and any other debts you might need to repay.
Life Insurance is your way of looking after your loved ones when you’re gone.

What do most people use life Insurance for?
- Paying off the mortgage. Many people need to reduce their debt as quickly as they can if they go from two incomes to one.
- Providing future financial support for their children. For example, someone could use part of their life insurance payment, after becoming terminally ill, to pay for their children’s tertiary education.
- Providing extra income for their family after they’ve gone, or contributing to their spouse’s retirement fund. Many people would need financial support if an income earner passed away.
- Paying for childcare support if the person who passed away was the primary caregiver. Many people find that, as the remaining parent, they need extra support. If they continue working, they may also need more childcare support.
3. What are the benefits of life insurance?
- It helps protect your family’s finances by providing your family with financial resources in the event of your untimely death and will pay your beneficiaries money to ensure they can continue to be financially supported.
- Tax-free one-time payment. Under New Zealand tax laws, you do not pay any income tax on any life insurance benefits you receive, provided they are taken out for personal use. This means that, following receipt of the benefit, the policy owner is not required to declare the lump sum payment to Inland Revenue, as no liability for income tax for the payment exists.
- Terminal Illness Benefit If this is included in your policy and you are diagnosed with a terminal illness with a life expectancy of fewer than 12 months, the Life Cover benefit is paid early in a lump sum.
- Peace of Mind Enjoy life knowing that you are looking after the people you love and the things you have worked hard for if life doesn’t go to plan.
- Dignity: In the event of a premature death your family’s dignity is and lifestyle is retained and they will not be forced to sell the family home, move schools and or suburbs due to financial stress.
Additional features that your Life Insurance contract may include:
- Terminal illness cover: you can get an advance on all or some of your sum assured if you’re diagnosed with less than 12 months to live.
- Funeral costs cover/bereavement support: your policy’s beneficiaries can apply for an advance to cover immediate costs such as funeral expenses. Access to this benefit will depend on who is the owner of the policy.
- Children’s funeral costs cover: you get a limited payment to cover funeral costs if your child dies from accidental injury. Some policies also cover death from certain illnesses.
- Increased sum assured due to certain major events: you can increase your sum assured by a pre-agreed amount without having to provide further medical information if you experience a major life event. Although it varies from policy to policy, common events include getting married or divorced, having children or taking out a home loan.
- Financial advice cover: you or your policy's beneficiaries can get financial advice (up to a limit) if the insurer pays out the sum assured.
4. Different Types of Life Insurance Explained
There are many different options for buying life insurance but it’s actually not as complicated as it may seem. When it comes down to it, there are essentially two kinds of policies: term life insurance and whole life insurance.
- Term life insurance lasts for a specific amount of time (the term) and expires at the end of the term. The term can be anything up to aged 100.
- Whole life insurance, on the other hand, is a form of permanent life insurance and lasts your entire life. Whole of Life is not available in New Zealand anymore, although there are many existing contracts in-force. If you have to assist to settle a parent’s estate, you may well find they have one of these policies in force.
The most common type of life insurance is 'term life’, which provides cover for a period of time such as 25 years or to a specific age, such as 70 or 80 or until your death. Term life insurance pays your estate or your chosen beneficiaries the sum assured if you die within the period set out by the policy.

5. How is a life insurance premium calculated in NZ?
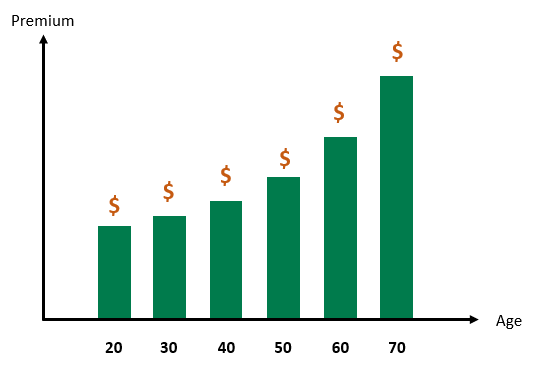
- Rate for Age or Yearly Renewable Term - Annual (or yearly) renewable term is a one-year policy, but the insurance company guarantees it will renew the policy on each anniversary up until an agreed age, regardless of the health of the insured person, and with a premium set for the applicant’s age at that time. The key thing is yearly stepped premiums increase each year in line with your age. Rates are for all people of a similar age and condition at policy commencement.
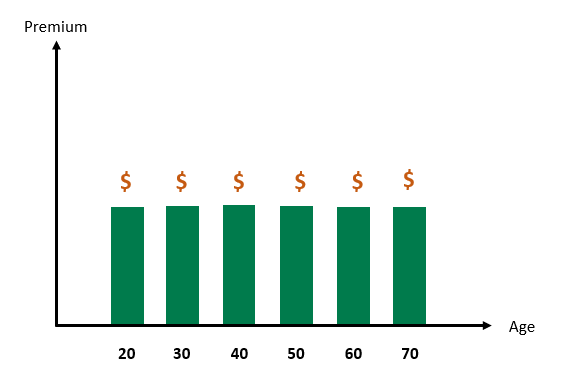
- Level cover is a multi-year policy, where the premiums are fixed at the start and stay the same for the agreed period. Most commonly fixed premiums until age 65, 70 or 80. The insurer guarantees the premiums and cover amount will not increase, but this type of policy will be more expensive initially.
You can select to index link a policy. Indexation is an automatic annual increase to the amount of insurance cover you have, to make sure the value of your cover is not eroded by the impacts of inflation. Your premiums will also increase when the cover increases if you elect to include this benefit.
Or you can choose a hybrid structure - a combination of both level and yearly renewable term premium structures can sometimes be smart – talk with your financial adviser to structure the best cost-effective insurance policy.
Generally speaking, the level premium cost more to start with compared with the rate for age insurance but when you get older, your premiums will continued to be affordable.

6. How much does life insurance cost in NZ?
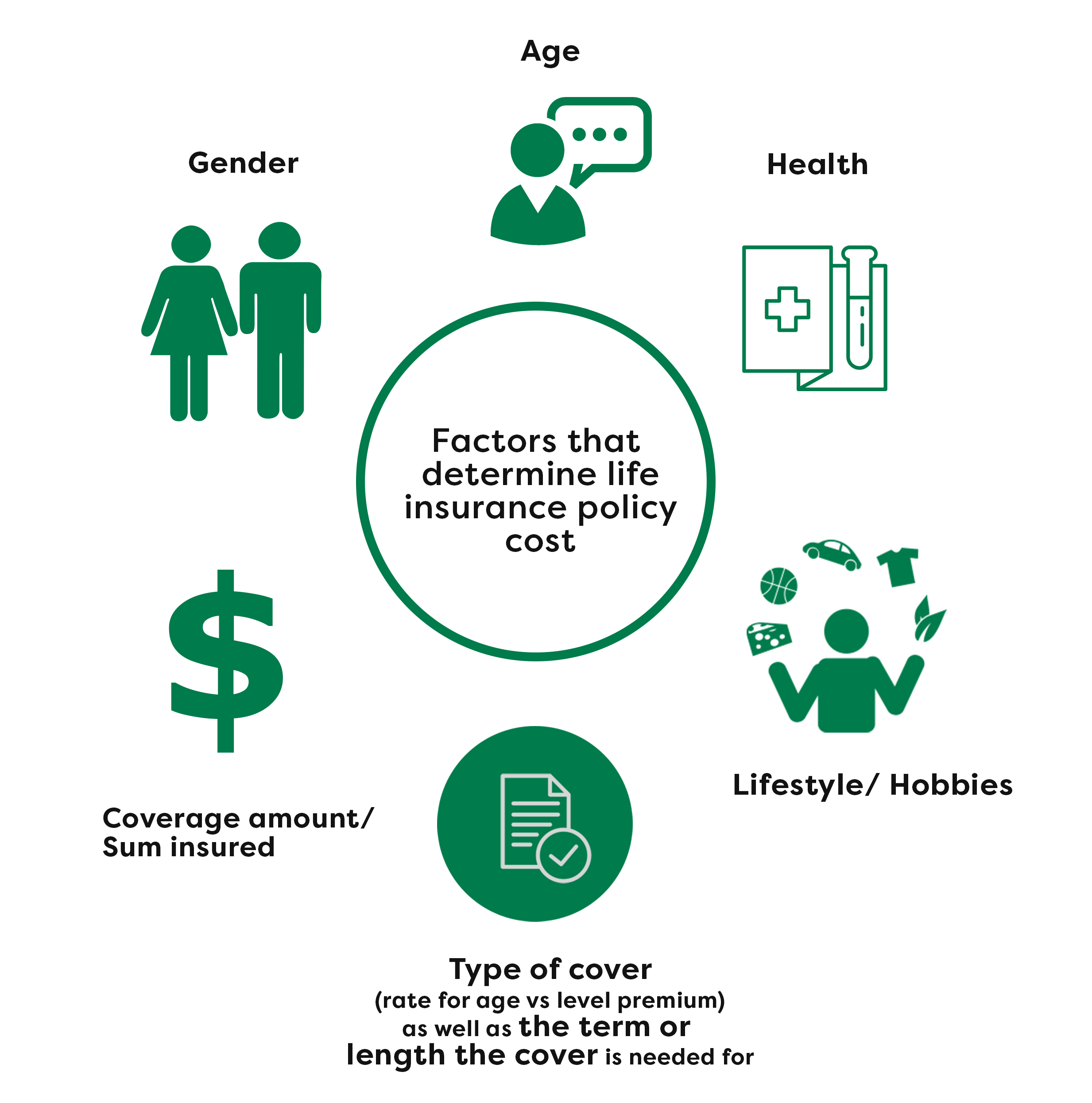
There are a number of factors that contribute to the price of your life cover policy. Understanding this can help make the application process smoother and ensure you make the best decision, both in value for money and protection for your family.
Some of the factors that determine the life insurance policy cost:

7. Life Insurance Checklist
1. Read our complete life insurance guide: Make sure you read through our 'Good to know' guide about life insurance. You can download the full PDF version from here.
2. Shopping for cover: get at least 3 quotes. Premiums can differ by hundreds of dollars. Remember that a policy that is the cheapest when you purchase it may well become the most expensive later-on, so it is worth looking at the overall cost over the expected life of the policy.
3. Ensure any pre-existing medical conditions that can be covered are covered. If you have a pre-existing health condition and or undertake a hazardous pursuit e.g. motor bike racing you may well have to pay an increased premium (a premium loading) due to the increased risk to the insurer.
4. In short, speak to an expert like a qualified Financial Adviser. Most Financial Advisers that are not employees of a financial institution, will have access to all the major providers in New Zealand.
5. Ask your insurer or your Adviser if there's anything in the policy you're unsure about and get them to explain it to you. Make sure you do this before you sign.
6. When you have insurance: keep the policy in a safe place - where your will is kept, or with your lawyer - and let your partner or family members know about it.
7. Every few years, review how much cover you need, particularly after major life changes such as marriage or divorce, having children, or children leaving home and becoming independent and maybe if you are really lucky after you win Lotto!
8. If you are changing insurers, don't cancel your old cover until you have been confirmed as a customer of the new insurer and have accepted their terms and conditions.
9. Life insurance can be a long-term purchase and in the long run you want a company that actually meets its contractual obligations (i.e. pays claims). That’s why we recommend that you only look at Insurance companies in New Zealand with a financial strength rating of A- or higher.
Key Things to Consider before getting Life Insurance
Getting the right cover level is the most significant consideration
We strongly recommend that you talk with a financial adviser to understand what level and type of life insurance will best protect you and your family.
Shop around
When it comes to buying life insurance, shop around. In some instances, we found price comparison sites quoted the same policies offered by the insurers directly for HALF the price. A 30-year-old male/female non-smoker should be able to get a $500,000 policy for under $400/year by shopping around. As to be expected, policies get more expensive the older you are.
Talk with Financial Advisers
Financial Advisers offer expertise and know the market more than anyone - if you have a specific concern, health issue or question about anything related to life insurance, they will likely be your best resource and asset for picking the best policy.
At HealthCarePlus, we have access to a nationwide team of Monument Financial Advisers. For over 30 years Monument Insurance has been HealthCarePlus’s appointed business partner to provide financial advice to HealthCarePlus Members on life and health insurance. So if you’d like to talk to one of them from your area, you can book a time for a free no obligation chat about your circumstances and what could be right for you.
Special Events
Increase Facility Enables you to increase the sum assured under your plan without the provision of medical evidence following a significant event in your life which results in increasing financial responsibilities. These significant events include: having a child, your child starting secondary school, taking out or increasing a residential home loan or receiving a salary increase and other major events covered.
Additional Trauma Cover
Sometimes called Critical Illness Cover (includes about 50 different illnesses and treatments), can be added to the life cover at an extra cost when you take out your life insurance policy.
Rate for Age & Level Premium combination
Some plans allow you at any time, to convert all or part of your Life Cover benefit from a Rate for Age premium structure to a Level premium structure without any further medical evidence.

